取消
自定义
功能亮点

模板优质
这里有许多专业设计的、可完全自定义的宣传册模板,并且会持续性更新。你可以免费使用模板来设计自己的宣传册。

资源丰富
我们拥有一个庞大的资源库,包含数量丰富的字体、形状、图标资源,可以帮助你设计宣传册。快来试试吧!

功能强大
DesignCap功能强大的编辑工具让你能轻松上传图片、编辑图片和文字。只需轻点几下鼠标,就能完成一个宣传册设计。

便宜实用
DesignCap为你提供了大量免费资源。即使预算不多,也能随意设计出你想要的宣传册。
如何在三步之内设计一个完美的宣传册
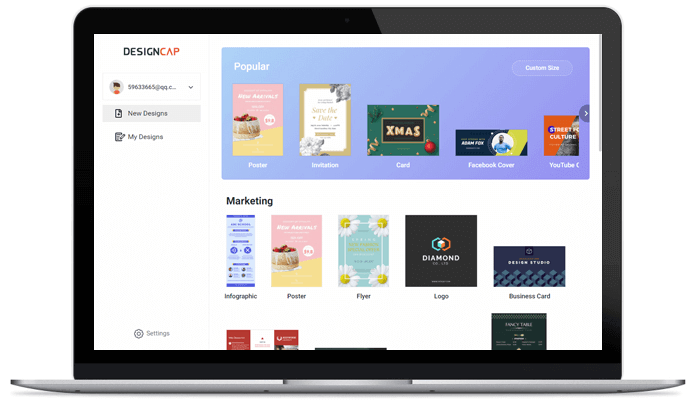
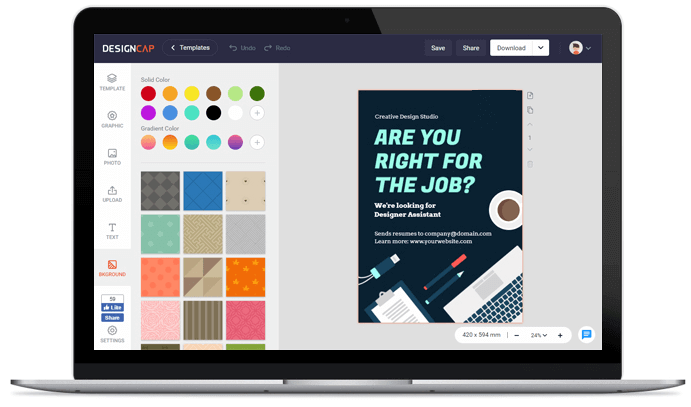

1. 选择模板
选择一个合适的模板,然后开始设计宣传册。
2. 自定义
使用功能强大的编辑工具和丰富的图形资源修改模板,使其符合需求。
3. 输出
保存设计的宣传册到电脑或在线分享。
用户评价

简单而实用的网站,它可以在线制作心仪的海报或传单,通过模板可以快速创建简约、美观的作品,并可以下载印刷级清晰度的图片文件!


DesignCap是一个在线制作海报的网站,可以使用模版(有多种场景模版贡供选择),然后“傻瓜式”操作替换文字部分即可,也支持你二次排版设计。


DesignCap提供了大量模板,能帮助用户可以轻松完成海报,贺卡,Facebook封面,YouTube横幅等各种极具个性化的设计。










